Hangzhou and Shaoxing, China, 12 April, 2021 -- Ascletis Pharma Inc. (HKEX:1672) announces today that four clinical and preclinical study abstracts of NASH and HBV have been accepted by the International Liver Congress™ 2021 as poster presentations. The summary of the four abstracts are shown as below:
1. Title: Significant lipid lowering by ASC41 oral tablet,a liver targeted THR-β agonist,in a Phase I randomized,double-blind,placebo controlled single- and multiple-ascending dose study
Abstract/poster number: 1851
Category: NAFLD therapy
Results: In the single-ascending dose portion of the study, preliminary data suggest that ASC41 is safe and well tolerated up to a dose of 20 mg. Furthermore, ASC41 tablet formulation showed a dose-proportional pharmacokinetic profile from 1 mg to 20 mg. In the multiple-ascending dose (MAD) portion of the study, preliminary data suggest that after 14 days of once daily oral dosing, subjects demonstrate clinically meaningful and statistically significant reduction in LDL-C and triglycerides compared to placebo, as shown in the table below.
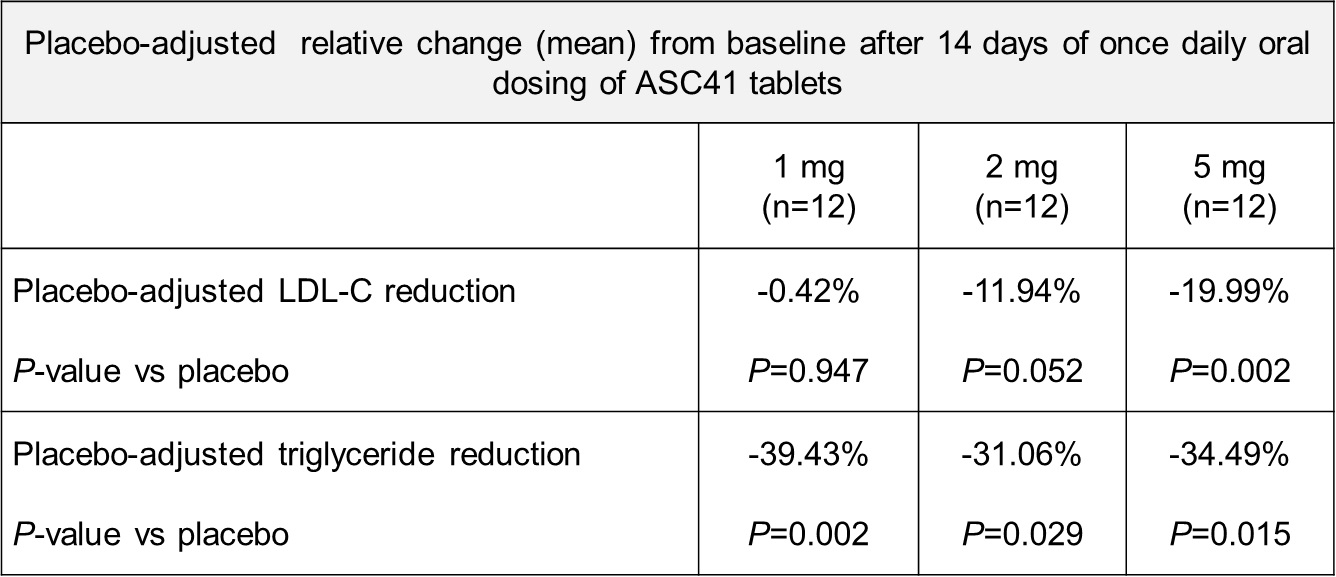
ASC41 had a benign adverse event profile at all doses following 14-day treatment, with no grade 3 or above adverse events, no serious adverse events or premature discontinuations. Furthermore, ASC41 tablet formulation displayed a dose-proportional pharmacokinetic profile from 1 mg to 5 mg following once daily, 14-day dosing.
Conclusion: These data supported advancement of the ASC41 clinical program for the indication of NASH.
2. Title: Significant improvement of NAFLD activity scores and liver fibrosis by ASC41, a selective THR-β agonist, in high fat diet induced NASH SD rats
Abstract/poster number: 1908
Category: NAFLD therapy
Results: ASC41 demonstrated dose-dependently reductions in liver steatosis, inflammatory cell infiltration, ballooning change and total non-alcoholic fatty liver disease activity score (NAS). ASC41 at 1.5 mg/kg and 4.5 mg/kg showed higher NAS reductions relative to MGL3196 at 5 mg/kg (P=0.01 and P<0.001). ASC41 at 0.5 mg/kg showed a 23.9% reduction in NAS score and a 14.4% reduction in liver fibrosis, similar to MGL3196 at 5 mg/kg. ASC41 at 1.5 mg/kg and 4.5 mg/kg both showed a significant decrease in serum LDL-C.
Conclusion: ASC41 demonstrated NAS reductions and anti-fibrotic benefits in the high fat diet induced NASH SD rats. The current efficacy data supported the advancement of ASC41 into clinical trials in human.
3. Title: Significant improvement of NAFLD activity scores and liver fibrosis by ASC42,a novel non-steroidal FXR agonist,in high fat diet induced NASH mice
Abstract/poster number: 1961
Category: NAFLD therapy
Results: ASC42 demonstrated dose-dependently reductions in liver steatosis, inflammatory cell infiltration, ballooning change and total non-alcoholic fatty liver disease activity score (NAS). ASC42 at 30 mg/kg showed a significantly higher NAS reduction relative to OCA at 30 mg/kg (P<0.001). ASC42 at 3 mg/kg showed a 46.2% reduction in NAS score and a 15.2% reduction in liver fibrosis, similar to OCA at 30 mg/kg. Total glyceride in liver exhibited a dose-proportional decrease in ASC42-treated mice.
Conclusion: ASC42 demonstrated NAS reductions and anti-fibrotic benefits in the mice NASH Model. These data supported the advancement of ASC42 into clinical trials in human.
4. Title: Significant in-vitro and in-vivo inhibition of HBsAg and HBV pgRNA with ASC42,a novel non-steroidal FXR agonist
Abstract/poster number: 1917
Category: Viral hepatitis A, B, C, D, E: virology
Results: In PHH model, the control compound ETV showed the expected inhibitory activity on HBV DNA, but had no inhibition on HBV pgRNA and HBsAg, while ASC42 inhibited HBsAg, HBV pgRNA, and HBV DNA dose-dependently, with EC50 of 0.79μM, 0.09μM and 0.62μM, respectively (Figure 1A-D). In AAV/HBV mice model, after ETV (0.1 mg/kg) monotherapy, HBV DNA in mice plasma decreased significantly, while HBV pgRNA and HBsAg showed no obvious reduction. ASC42 demonstrated a dose-dependent inhibition of HBV pgRNA, HBsAg, HBV DNA in mice plasma. High-dose group of ASC42 (60 mg/kg) inhibited HBV pgRNA, HBsAg, and HBV DNA by 0.60 log10 copy/μl (P<0.01), 0.38 log10 IU/μl (P =0.002), and 0.77 log10 copy/μl (P <0.05), respectively, relative to vehicle control group (Figure 1 E-F).
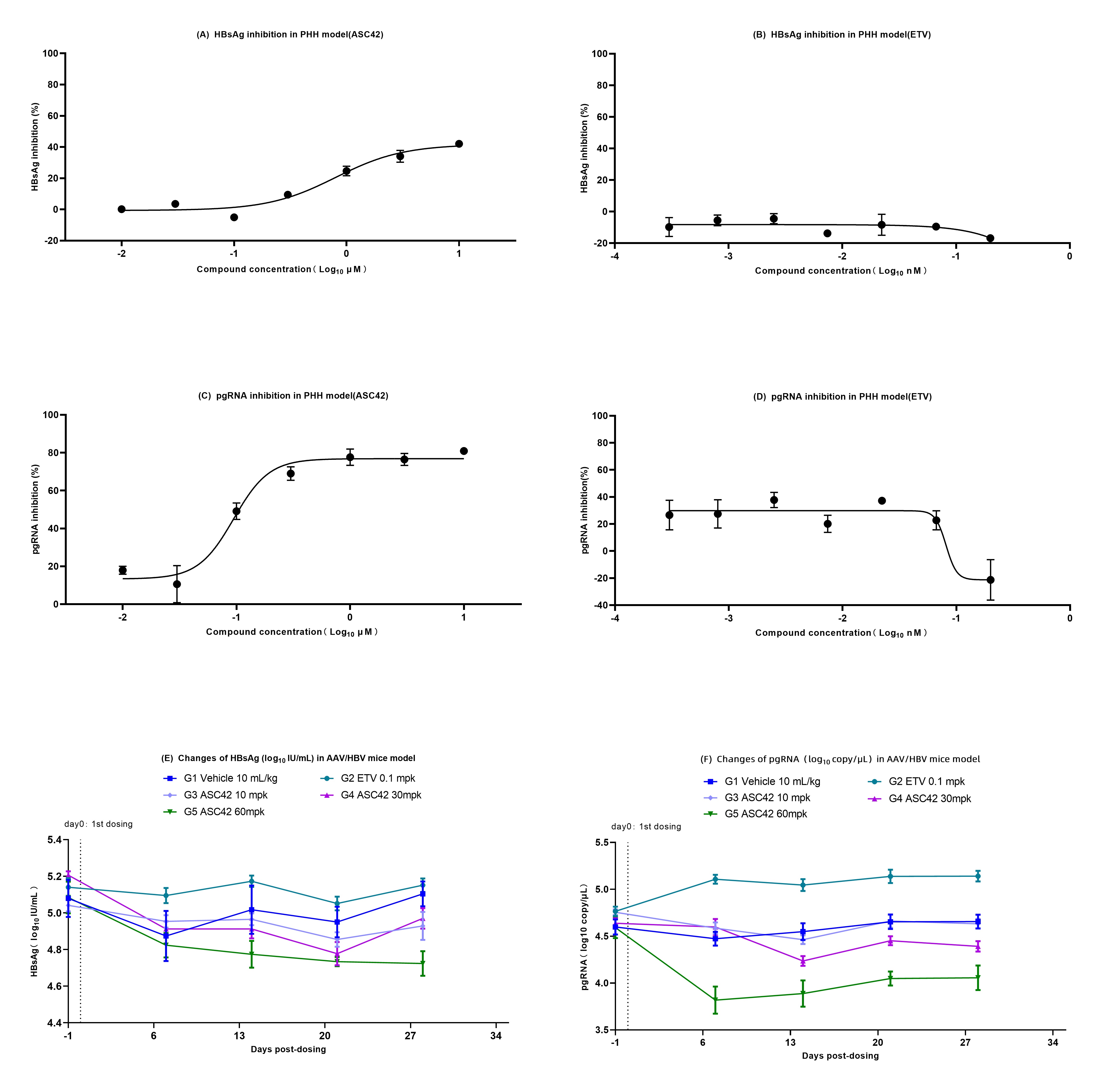
Conclusion: These in-vitro and in-vivo studies demonstrated that ASC42, a FXR agonist, significantly inhibited HBV DNA, HBV pgRNA and HBsAg, indicating that ASC42 has therapeutic potential to functional cure of HBV infection. The results support the advancement of ASC42 into clinical trials in human.